Sitemap.xml link selector can be used similarly as Link selector to get to target pages (for example product pages).
By using this selector, the whole site can be traversed without setting up selectors for pagination or other site navigation.
The Sitemap.xml link selector extracts URLs from sitemap.xml files which websites publish so that search engine crawlers can navigate the sites easier.
In most cases, they contain all of the sites relevant page URLs.
Web Scraper supports standard sitemap.xml format.
The sitemap.xml file can also be compressed (sitemap.xml.gz).
If a sitemap.xml contains URLs to other sitemap.xml files, the selector will work recursively to find all URLs in sub sitemap.xml files.
Note! Web Scraper has download size limit. If multiple sitemap.xml URLs are used, scraping job might fail due to exceeding the limit. To work around this, try splitting the sitemap into multiple sitemaps, where each sitemap has only one sitemap.xml.
Note! Sites that have sitemap.xml files are sometimes quite large.
We recommend using Web Scraper Cloud for large volume scraping.
sitemap.xml files. Multiple URLs can be added. By clicking on "Add from robots.txt"
Web Scraper will automatically add all sitemap.xml URLs that can be found in sites https://example.com/robots.txt file.
If no URLs are found, it is worth checking https://example.com/sitemap.xml URL which might contain a sitemap.xml file that isn't listed in the robots.txt file.sitemap.xml that
match RegEx will be scraped.sitemap.xml file to decide if this value should be filled.Sitemap.xml files are usually used for sites that want to be indexed by search engines, sitemaps can be found for most:
Best way to scrape the whole site is by using Sitemap.xml link selector. It removes the necessity of dealing with pagination, categories and search forms/queries. Some sites don't display category tree(breadcrumbs) if the page is opened directly. In these cases site has to be traversed through category pages to scrape the category tree.
As in most cases, sitemap.xml contains all pages of the site, it is possible to limit the scraper so it scrapes only
the pages that contain the required data. For example, e-commerce sites sitemap.xml will contain of product pages,
category pages and contact/about/etc. pages. To limit the scraper, so that it scrapes only product pages, one or more methods
can be used:
/product/. This will prevent
the scraper from traversing and scraping unnecessary pages.Using wrapper element selector - if none of the previously mentioned methods are possible, an element wrapper selector can be set up. This method works for all sites and doesn't return empty records in the result file if invalid or unnecessary page is traversed. To set up the element wrapper selector, follow these steps:
h1.product-title.multiple and set its selector to (for example) body:has(h1.product-title).The key part of this method is that a unique element has to be found and included in body:has(unique_selector)
selector. If the data from meta tags has to be scraped, html tag can be used instead of body tag. Scraper will
extract data only from the pages that have this unique element.
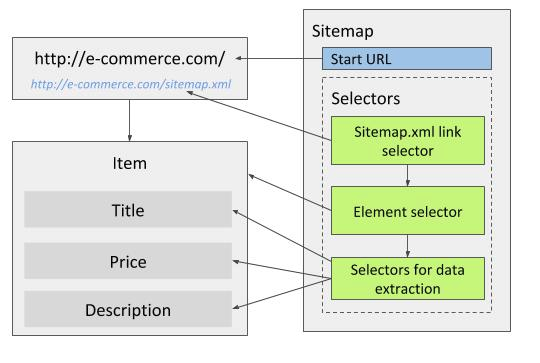
When using Sitemap.xml selector, set the main page of the site as a start URL.